Table of contents:
What is VoIP?
What does VoIP stand for? VoIP, meaning Voice over Internet Protocol or Voice over IP, is a technology that enables the transmission of voice over an internet connection.
A VoIP phone system first converts a speaker’s voice from audio waves into digital data, it then sends that data to its destination via a network connection. If that destination is a regular telephone network, the signal is converted back to a telephone signal before it arrives there.
So what does VoIP mean for users? With the technology operating over the internet and other data networks, one of the greatest advantages of business VoIP phone service is that by leveraging the power of the cloud, VoIP providers like net2phone enable conversations with customers, suppliers,and employees wherever they are located, and using whatever device they prefer.
Types of Protocol Used in VoIP
Transport Control Protocol (TCP): Data packets are connected directly from source to destination and remain connected for the duration of the transfer. Highly accurate and guarantees delivery of packets in their original order.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP): A connectionless protocol which prioritizes speed over accuracy. UDP has no control over errors but is useful for real time VoIP applications where a continuous stream of data is required.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP): A signaling protocol which informs a VoIP system to initiate, maintain, and terminate communication sessions. Also responsible for defining the format of messages and the sequencing of communication.
Related: What is SIP Trunking and How Do SIP Trunks Work?
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP): Used in conjunction with SIP to deliver audio and video over IP. Typically runs using UDP but also employs a Real-Time Transfer Control Protocol (RTCP) to monitor transmission statistics and quality of service.
How is VoIP Different from a Traditional Phone System?

Rather than relying on a telephone company’s wiring, IP telephony, internet telephony, or web calling converts voice calls and other multimedia content into digital data, which can then be transmitted over the internet, local area networks (LANs) or wide area networks (WANs). In this way, VoIP lines enable users to make voice calls.
VoIP
|
Landline
|
|
Transmit voice data packets via internet.
|
Requires physical hardware such as copper lines to function.
|
|
Require a steady electrical supply, together with fast and stable network data connections.
|
Needs an analog phone (physical device) connected to PSTN.
|
|
Maintenance costs are also kept to a minimum because everything is hosted digitally in the cloud.
|
Simple to operate, and most people are comfortable with using them.
|
|
Offering remote working options is easier than ever as employees simply need to log in from any location and can make and receive calls as if they were in the office.
|
More secure as there are fewer points of failure, and they are less prone to social engineering type scams.
|
This is quick break down of the main differences between VoIP and Landline phone systems. More detailed explanation, you can find in our guide below.
Find more detailed comparison: VoIP vs Analog Phone System
WebRTC, SIP, PBX are not VoIP. What Makes Them Different?
Here is a list of other technologies sometimes called VoIP, but are not:
WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication) is a technology very similar to VoIP. It also allows users to make and receive calls as well as other multimedia data but only using a web browser. VoIP does the same via installed software or an App.
SIP Session Initiation Protocol is not a technology, but the most important component in VoIP phone system. It is responsible for setting up connections between different devices including computers, VoIP, landline, and mobile phones.
Cloud PBX stands for Cloud-based Private Branch Exchange and refers to a virtual PBX system that works together with VoIP and hosted on the internet. It answers the calls and routes them to the right department or user extension.
What is a VoIP Phone?
A VoIP phone is any hardware or software that uses VoIP technology to make and receive calls over the internet. This can include a physical phone, a mobile phone, or a desktop computer or laptop. This technology has grown in popularity and allows businesses to connect with customers, partners, and prospects like never before.
What is VoIP Call?
In practical terms, VoIP call means converting voice signals into digital signal that is then transferred over a data network. At its destination, the IP call data is translated into a regular phone signal.
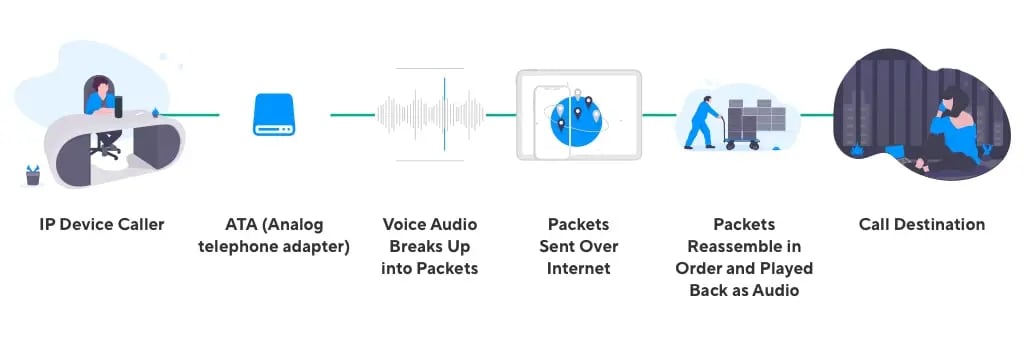
In general, there are three principal mechanisms for making a phone call over the internet :
- An analog telephone adaptor (ATA) lets you connect a standard phone to your computer or internet connection, and acts as an analog-to-digital converter. A cable connection from your handset to the ATA (and perhaps the installation of some software, depending on the manufacturer), enables IP telephony.
- IP phones with an RJ-45 Ethernet connector look and feel like normal phones, but connect directly to your network router, and come with all the necessary hardware and software for making IP calls.
- Peer-to-peer or computer-to-computer connections use software as the medium for making phone calls over the internet. An internet connection, sound card, microphone, and speakers are the required physical infrastructure.
What is a VoIP Caller?
A VoIP caller is simply someone who is calling you using a voice over internet system, rather than a conventional phone network.
To identify a VoIP caller, you can use a reverse phone look-up service. If you use a VoIP phone with a packet analyzer, this can display the IP details of each call you receive, and look up the associated IP address.
What is a VoIP Number?
Also known as a virtual phone number, a VoIP number is a telephone number that is assigned to a specific user, rather than a specific phone line.
We have already observed that voice-over IP is largely a location-independent system. Area codes have no particular relevance to VoIP phone numbers. In fact, VoIP users can choose a phone number with any area code. This enables businesses to establish a local presence in different regions, which can be very lucrative for businesses.
How Does a VoIP Phone System Work?
An Internet Protocol call is routed via an internet or data network connection.
So, instead of being tied to a specific location, area code, or device VoIP or Voice over IP calls can be made using a smartphone, tablet, laptop, desktop computer system, or landline phone with a converter — as long as a stable data connection is available.
In general, there are two principal mechanisms for making a phone call over the internet.
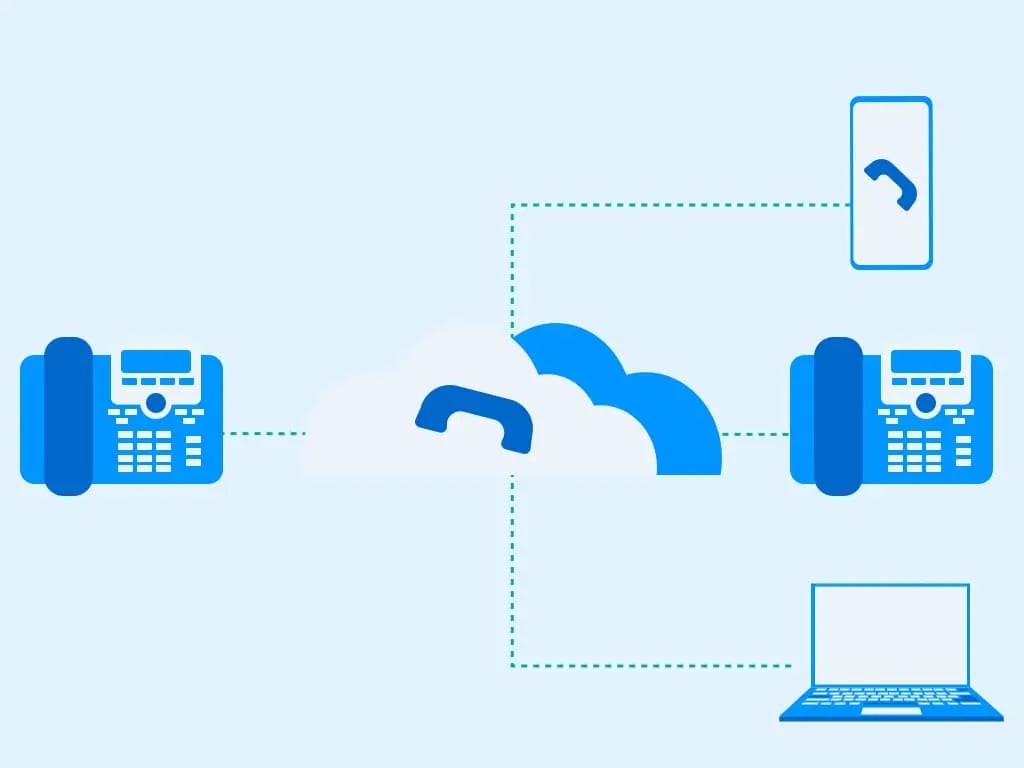
How Do VoIP-to-VoIP Calls Work?
When you talk on a VoIP line, your device converts voice into data packets. The data packets are then sent over the internet to the receiver through your internet service provider. The data packets are then decoded and output as audio to the receiver.
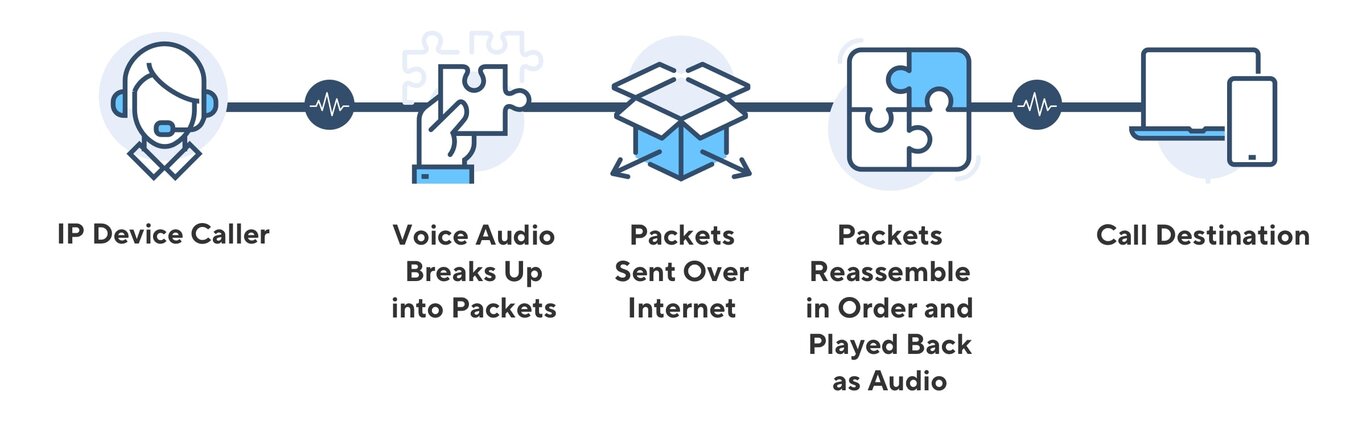
How Do PSTN-to-VoIP Calls Work?
While VoIP uses data packet switching to connect calls, PTSNs use circuit switching. Calls originating through a PTSN will run smoothly, as carriers convert the calls from analog voice signals into digital signals which will then be compressed into packets transferred via the IP network. The reverse process occurs when making calls from a VoIP service to an analog recipient.
Advantages & Disadvantages of VoIP
What is the advantage of using VoIP calling?
As we have already learned, one of the major advantages of voice over ip calling is being able to use a data network or internet technology for communications transmission. VoIP users can have conversations through the power of the cloud, which facilitates communication exchanges all over the world- wherever they are located, and with whatever device they prefer.
However, that’s just one of the plus points. In this section, we’ll take a look at the various VoIP advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of VoIP
-
Cost Savings: VoIP users save on the costs of installing and maintaining physical infrastructure, as they don’t need to manage the hardware and cabling associated with a conventional phone system. Using an internet connection, the cost of VoIP international calls and domestic phone calls is also drastically reduced, when compared to traditional phone charges.
-
Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud-based VoIP phone systems allow businesses to extend full communications functionality to remote workers and geographically dispersed sites. Voice over IP services enable enterprises to quickly and easily increase or decrease their number of users and communications features, in response to changing conditions, without the need to add physical infrastructure.
-
Easy to Install: The installation timeline not weeks, days, even hours, it can be installed in mere minutes. Installation can be done without an onsite technician as everything is run through an existing internet connection.
-
Number Portability: Most reliable VoIP providers will enable users to keep their existing local business phone numbers, even if they move to a different service. Voice over IP users typically have access to more numbers than with the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
-
An Abundance of Features: As we’ll discuss in the next section, VoIP systems offer a multitude of enterprise-class communications features.
Disadvantages of VoIP
-
Reliance on Power and Internet: VoIP technology relies on a steady electrical supply, together with a fast and stable network data connection. An outage or disruption to either of these utilities can lead to dips in the performance of voice over internet, or even complete loss of the service.
-
Potential Connectivity Issues: Even though super-fast broadband and leased line connections are widely available in much of the world, there are still regions where internet connectivity is unreliable, or even non-existent. In such areas, issues with latency (data transfer delays) and packet loss can lead to a deterioration in call quality and data transmission.
Top Features of a VoIP Phone System
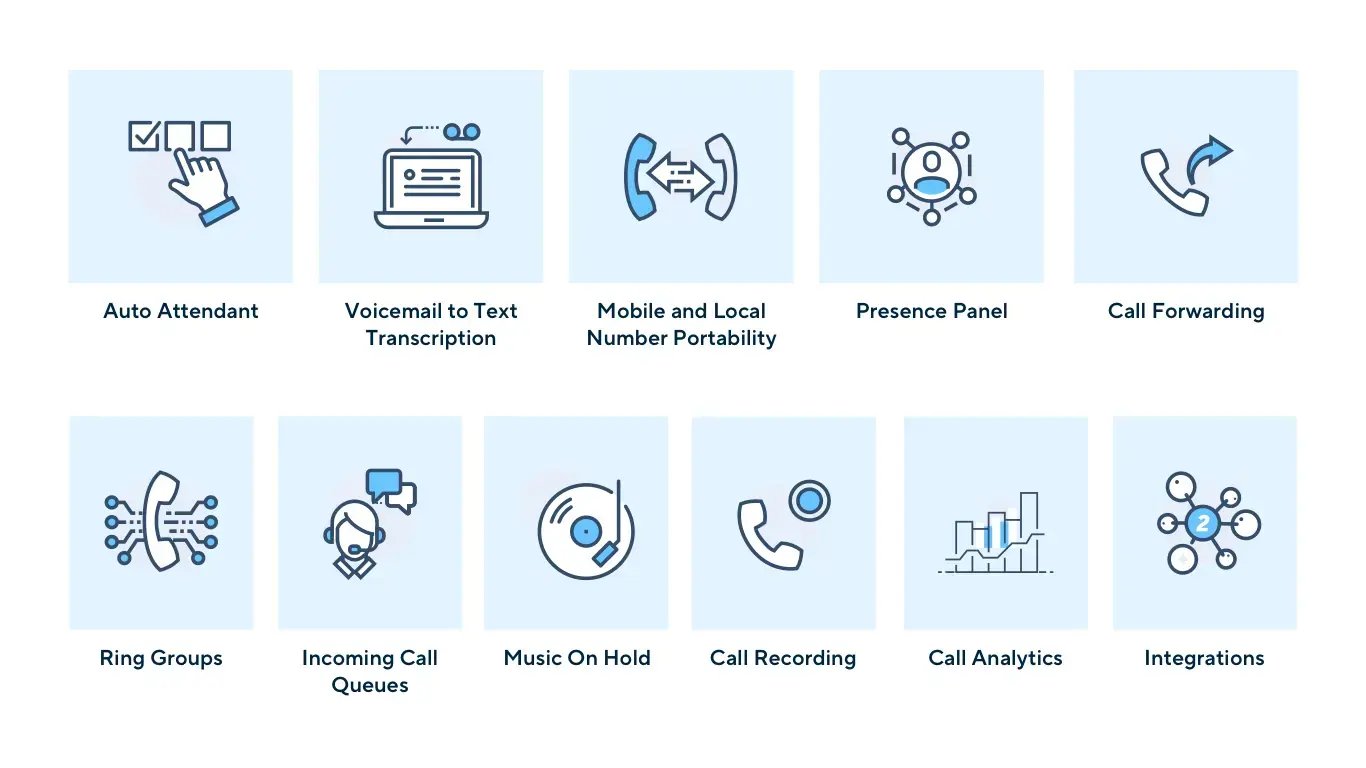
Voice-over IP calling tends to come with many robust features when provided by a business-class VoIP system, such as net2phone. Main IP-based calling features usually include, but are not limited to the following:
-
Auto-Attendant - “Electronic receptionist” with advanced call handling and routing.
-
Voicemail to Text Transcription - Access your voicemail messages even easier by receiving them as transcribed text sent via email or text message.
-
Mobile and Local Number Portability - Moving from another phone system? Keep your existing numbers and extensions and we’ll port them for free.
-
Presence Panel - Displays who is available to take a call, who is busy, etc.
-
Call Forwarding - Create rules that automatically route callers to the next available person or department based on criteria you set.
-
Ring Groups - Allows all extensions in a group to ring simultaneously.
-
Incoming Call Queues - Allows calls to be distributed and routed accordingly.
-
Music On Hold - Let your callers hear music, recorded audio, or customized marketing messages while they are placed on hold.
-
Call Recording - Enable call recording to log and save your calls so you don't miss important details, or to use the interactions for employee training.
-
Call Analytics - Analyze calling traffic and history, user statistics, identify patterns and trends, and enable smarter business conversations with full visibility.
-
Integrations - Since VoIP is a digital solution, it can connect to other SaaS tools such as your CRM or video conferencing software through integrations. This creates a unified system where each solution communicates and interacts with the other.
Concerning VoIP features, net2phone President Jonah Fink observes, “Just as the young millennials are relying on chat and messaging, we believe that the business community will do the same and we very much look forward to bringing them the ability to use alternative methods of communicating, along with our hosted voice, all in a single offering. We are constantly evolving our product set and improving our channel partner tools to meet today’s ever-changing needs as we prepare for tomorrow’s demand. net2phone is not looking to follow, we are looking to innovate.”
How Much Does a VoIP Phone System Cost?
Price levels for internet calling vary widely from one VoIP provider to another. VoIP calls may be free or they may come with a charge. In the VoIP industry, the standard practice is to pay a monthly or annual fee for all of your lines.
To give you an idea about VoIP and traditional phone system costs we compared their initial and monthly costs, device costs, and international calling costs.
VoIP
|
Traditional Phone System
|
|
Initial costs: $0-$19.99 per line
|
Installation fee: $50-$99.99
|
|
Monthly costs: $17-$29 per line
|
Deposit: $50-$400 per line
|
|
Device costs: Free (for some plans)
|
Maintenance monthly fee: $80+
|
|
International calls: Free to 40+ countries. $0.01+ per minute to other
|
International calls: $1.00+ per minute
|
How Much You Can Save Using VoIP?
Businesses report huge cost savings when switching to cloud PBX – 90% saved on international call bills, 40% on local phone bills, and 75% on operational costs, equating to $1,200 of savings for each phone line they have.

VoIP Phone System Equipment and Hardware
One of the main advantages of employing a VoIP solution is there’s not a lot of equipment required to facilitate it. There are however one or two pieces of hardware which are essential/nice to have.
Essential Equipment and Hardware
A device from which to run the VoIP platform and initiate calls is essential to a functioning VoIP system. With many communications providers this can be a:
-
desktop phone
-
computer, (laptop or desktop)
-
mobile device (smartphone, or tablet).
Any connected device which is compatible with your service provider can be used to make calls. If you are calling from a busy office or contact center, you will want either a headset or a handset to make calls.
Customer privacy is important, so this will be essential for making customer-facing calls.
You will also need an internet connection. If using a mobile device, this can either be a mobile internet protocol such as 5G or any WiFi you might have access to. In an office setting, you will require a commercial internet package and ample ethernet ports for the device you have installed.
Optional Equipment
You may decide you prefer a physical device from which to make calls, in which case you will need a VoIP hard phone. This type of device looks very much like a traditional landline telephone but will often carry VoIP specific features such as call transfer, multiparty calling, and support for multiple VoIP accounts.
Selecting the Right VoIP Phone System for Your Business Needs
Which is the best VoIP provider? The answer will depend on your needs, budget, and circumstances.
Here are some general tips for selecting the best business voice over IP providers:
- Identify the communications features that you need most.
- Take future expansion or business growth into account.
- Establish the size of your budget.
- Make a comparative assessment of voice-over internet providers, and what they have to offer.
- Look for testimonials, reviews, and customer referrals for the providers on your shortlist.
Don’t forget to factor in what kind of technical support they have available.
For Sole Proprietors And Micro-scale Enterprises
At the single owner or micro start-up stage, incoming calls are vital – so a customizable auto attendant phone system is a must. Call routing to your designated best numbers, or to your best qualified employees are the key features to look for. Custom messages for promotion and Music On Hold can help boost your image.
For Small Offices
For diverse small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) VoIP providers should offer small business phone system solutions with a variety of VoIP options together with calling features and levels of integration with web and mobile applications or office software.
For Large-scale Enterprises
Companies with large workforces and numerous phone lines should expect to see dramatic savings from VoIP – from 30 to as much as 90%. Shop around for a balance offering the best feature set and the highest savings.
For Dedicated Call Centers
If you operate a call center, many business VoIP providers offer dedicated products and packages to address your need for huge numbers of incoming and outgoing calls, reduced waiting times, comprehensive feature sets, and quality assurance.
Look for call recording facilities with analytics and reporting tools, to enhance your call monitoring and customer experience refinements. Manage customer calls and interactions directly with an intelligent cloud contact center.
For All Users…
The ideal VoIP solution should be fully capable of meeting all the operational and business needs you specify, with options to reconfigure or customize your subscriptions in response to changing conditions. Read our detailed guide 33 Questions to Ask When Choosing a Communication System to help you make your decision to find the right provider for your business.
From Analog to Digital - The History of VoIP
When it comes to the origins of VoIP, we can start with the introduction of analog communication in the 1930s. In analog communication systems, a continuous signal is carried through a time-based variable, like a voltage or pressure, to transmit voice, data, image, signal, or video information.
An example of analog communication is traditional, landline telephone systems. In this type of communication, sound waves are generated by a speaker’s voice and then transmitted into electrical signals that travel along a physical wire and are converted to sound waves that the listener can hear.
Moving forward, digital communication originated with the invention of computers in the 1950s, when communications could be transmitted, processed, and stored through digital signals. With digital systems, information is transmitted via digital signals that are discrete, either on or off, rather than continuous, and data is transmitted through point-to-multipoint or point-to-point channels, opening up new possibilities. Digital communication has many benefits over traditional, analog communication, including:
- Increased transmission range
- Greater sound quality
- Reduced chance of errors
- The ability to deliver more information
- Greater portability and flexibility
- Better security and encryption
This brings us to the introduction of VoIP in the mid-1990s, which first allowed users to make phone calls using their computers with an internet connection rather than a physical landline. This allowed for much cheaper long distance and international calls for businesses. Let’s dive deeper into what VoIP stands for and what it means.
Unified Communications - the Future of VoIP
This all brings us to the modern business communication solutions of today, unified communications, the future of VoIP. Unified Communications as a Service (UCaaS) brings multiple aspects of enterprise communications including voice, video, messaging, and voicemail, onto a single platform, accessible via the cloud.
With all-in-one UCaaS platforms, organizations don’t need to set up several different tools (for example a video conferencing solution, a business phone system, and a messaging platform). These tools are built into one single solution and are integrated to communicate with each other. Data is all stored on one interface rather than multiple places.
Tools like net2phone’s Unite UCaaS platform allow users to connect with calls, messaging, video, fax and more in one streamlined, unified communication solution.
UCaaS solutions offer businesses many benefits, including:
- Reduction of monthly subscription costs by not having multiple vendors for communication platforms
- Further reduced costs on installation and maintenance with software and updates deployed via the cloud.
- The ability to have a mobile workforce with technology that allows employees to connect from anywhere across the globe.
- Scalability to easily add users as businesses grow.
- Versatility to connect with prospects and customers through their channel of choice.
Even more data security and privacy.
Don’t get us wrong. While unified communications are the way of the future, this doesn’t mean that VoIP is dead. It has merely evolved with more advanced technology and innovations that allow businesses to grow, thrive, and keep up with changing customer needs and expectations. These modern solutions will surely pave the way for even more advanced business communication technology in the future, and we’re excited to be along for the ride.
To learn more, read our definitive guide to unified communications.